What Is Range Trading?
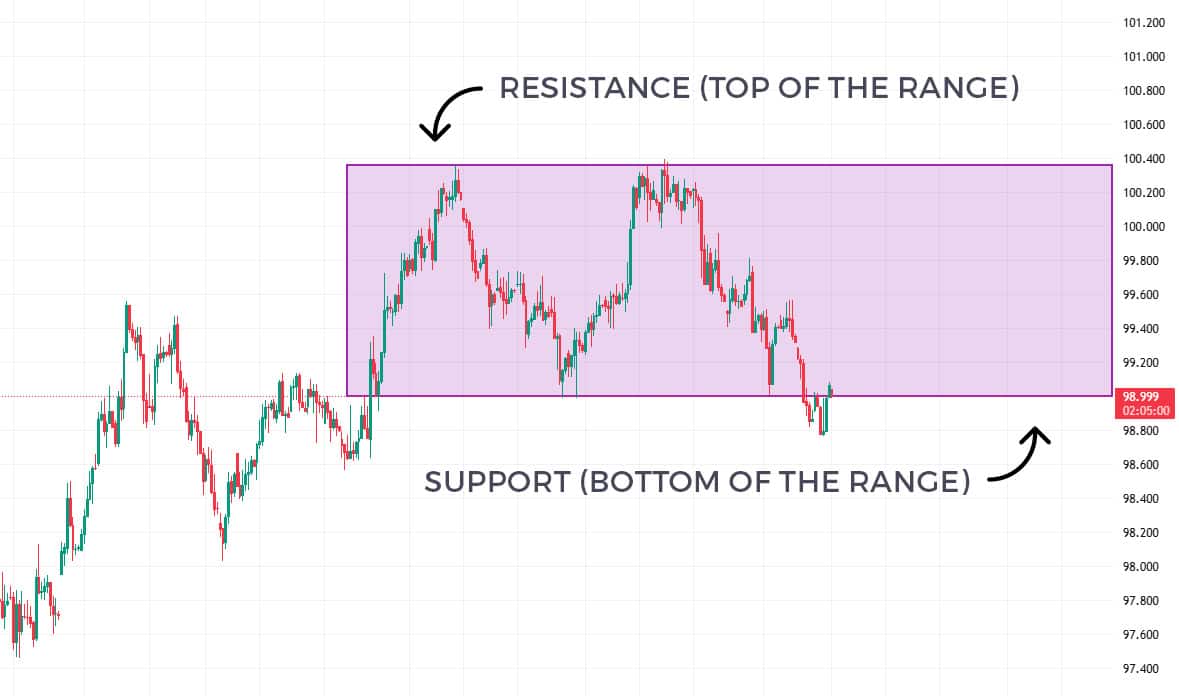
Range trading is a strategy where traders buy at the lower boundary (support) and sell at the upper boundary (resistance) of a sideways moving market. When prices are confined between these levels without breaking out in either direction, the market is said to be “trading in the range.”
Think of it like a ball bouncing between the floor and ceiling of a room. The floor represents support where buyers step in, and the ceiling represents resistance where sellers take control. As a range trader, your goal is to capitalize on these predictable bounces.
Key Components of a Trading Range
- Support Level: The lower boundary where buying pressure prevents further price declines
- Resistance Level: The upper boundary where selling pressure prevents further price increases
- Range Width: The distance between support and resistance, which determines profit potential
- Time Frame: Ranges can exist on any chart period, from minutes to months
Key Takeaway: Range trading works best in non-trending markets where price action respects established boundaries and shows consistent bouncing patterns.
How Does a Range Trading Strategy Work?
A successful range trading strategy follows a systematic approach to entering and exiting positions. The beauty of this method lies in its simplicity and clear-cut rules that beginners can easily follow.
The Basic Range Trading Process
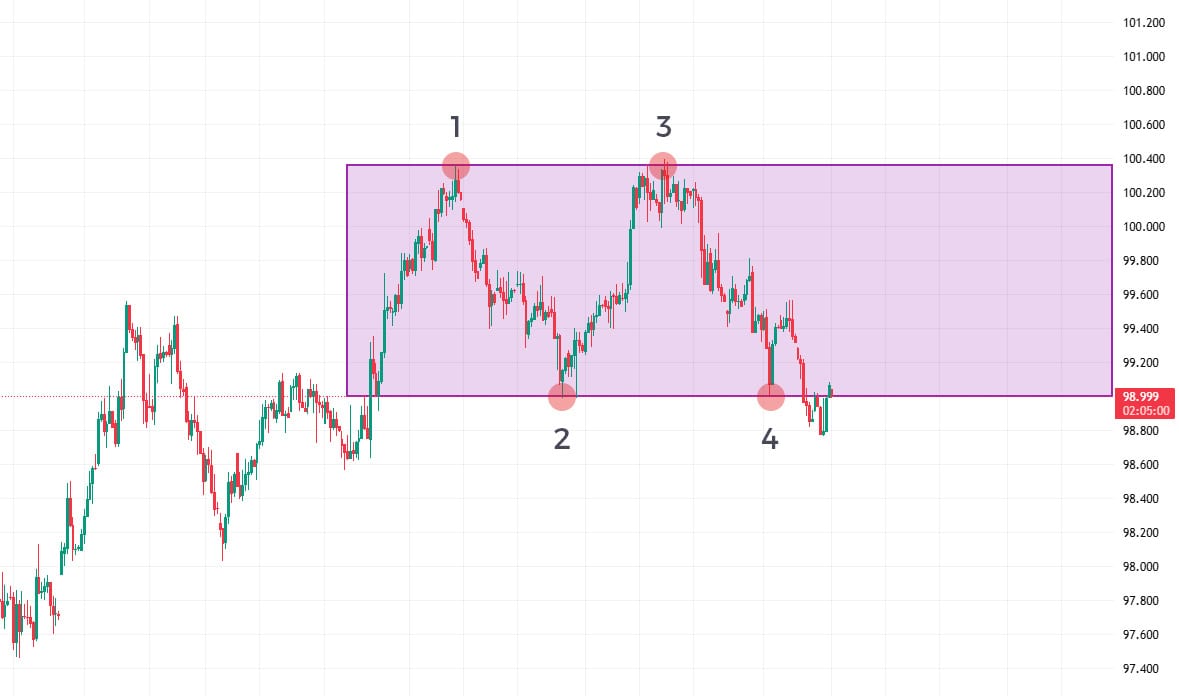
- Identify the Range: Find markets showing clear horizontal support and resistance with at least 2-3 touches on each boundary
- Wait for Price to Reach Boundaries: Exercise patience as price approaches either the support or resistance level
- Enter Near Boundaries: Buy near support with confirmation, sell near resistance with confirmation
- Set Clear Targets: Your target is the opposite boundary of the range
- Use Stop Losses: Place stops just outside the range to limit risk if the range breaks
Confirmation Signals to Look For
Before entering a range trade, watch for confirmation that the boundary will hold:
- Candlestick reversal patterns (pin bars, engulfing patterns)
- Increased volume at the boundary level
- Momentum indicators showing oversold conditions at support or overbought at resistance
- Price rejection wicks that test but don’t break the boundary
The range trading strategy becomes more reliable when you combine price action at boundaries with these additional confirmation factors rather than blindly buying and selling at the edges.
Understanding Box Range Trading
Box range trading is a specific variation where the support and resistance levels are particularly well-defined and parallel, creating a rectangular or “box” shape on the chart. This pattern offers some of the clearest trading opportunities for beginners.
Characteristics of Box Ranges
A true box range exhibits these features:
- Horizontal support and resistance lines that are roughly parallel
- Multiple touches on both boundaries (minimum 3-4 total touches)
- Relatively equal price swings between boundaries
- Consolidation period lasting days, weeks, or even months
Trading the Box Range
When trading a box pattern, your approach should be mechanical and disciplined. Enter long positions when price reaches the bottom 20% of the box and shows signs of support. Enter short positions when price reaches the top 20% of the box and shows resistance.
The middle of the box (50% level) often acts as a pivot point. If you miss an entry at the boundaries, avoid chasing trades in the middle zone where the directional bias is unclear.
What is the Daily Trading Range?
The daily trading range refers to the distance between the highest and lowest prices reached during a single trading day. Understanding this concept helps you set realistic profit targets and identify when a market offers sufficient movement for range trading.
Calculating Daily Trading Range
Daily trading range = High of the day – Low of the day
For example, if a stock reaches a high of $52.50 and a low of $50.00 in one day, the daily trading range is $2.50.
Why Daily Trading Range Matters
- Volatility Assessment: Larger daily ranges indicate more volatility and trading opportunity
- Position Sizing: Helps determine appropriate stop loss distances based on normal price movement
- Profit Targets: Average daily range indicates realistic profit expectations
- Range Selection: Assets with consistent daily ranges make better range trading candidates
Average True Range (ATR)
Professional traders often calculate the Average True Range over 14 or 20 days to understand typical volatility. If today’s range significantly exceeds the ATR, it might signal a breakout rather than a ranging day. Conversely, ranges much smaller than the ATR might indicate consolidation before a larger move.
Opening Range and Opening Range Strategy
The opening range is one of the most important concepts for day traders using range-based strategies. It refers to the high and low prices established during the first 15, 30, or 60 minutes of the trading session.
What Is Opening Range Strategy?
An opening range strategy is a tactical approach where traders identify the initial range created at market open and then trade either:
- Within the Range: Buying near the opening range low and selling near the opening range high
- Breakout Method: Trading breakouts above or below the opening range boundaries
Why the Opening Range Is Significant
The first minutes of trading often see the highest volume and volatility as overnight orders execute and traders react to news. The boundaries established during this period frequently act as support and resistance throughout the entire session.
Implementing Opening Range Strategy
Here’s a simple framework for beginners:
- Define Your Time Period: Use the first 30 minutes for stocks, 15-30 minutes for futures
- Mark the High and Low: Draw horizontal lines at the highest and lowest prices during the opening period
- Wait for Price to Test Boundaries: Be patient and let price come to you
- Trade the Bounce or Break: Enter when price bounces off boundaries with confirmation, or trade breakouts with volume
- Manage Risk Carefully: Use the opposite boundary as your target and place stops just outside the range
Many professional day traders rely exclusively on opening range strategies because they provide clear structure and defined risk from the market open.
Best Practices for Successful Range Trading
Now that you understand the fundamentals of range trading, let’s explore the best practices that separate profitable range traders from those who struggle.
Choose the Right Markets
Not all assets are suitable for range trading. Look for:
- Markets with clear sideways patterns and established boundaries
- Sufficient liquidity to enter and exit without slippage
- Adequate volatility to provide profit after transaction costs
- Stable market conditions without major news events pending
Risk Management Rules
Golden Rules:
- Never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single range trade
- Always use stop losses placed just outside the range boundaries
- Exit immediately if the range breaks with strong momentum and volume
- Take partial profits at the midpoint if the range is wide
Technical Indicators to Support Range Trading
While price action is primary, these trading indicators can help confirm range trading opportunities:
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Identifies overbought levels near resistance and oversold levels near support
- Bollinger Bands: Shows when price reaches extreme boundaries
- Stochastic Oscillator: Provides momentum confirmation at range boundaries
- Volume: Increasing volume at boundaries suggests the level will hold
When to Avoid Range Trading
Stay Out When:
- Major economic announcements are scheduled
- The market shows trending behavior with higher highs and higher lows
- Volume is unusually low, indicating lack of interest
- The range is too narrow to profit after transaction costs
- You see multiple false breakouts suggesting an imminent true breakout
Common Range Trading Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a solid understanding of range trading principles, beginners often fall into these traps:
1. Trading Without Clear Boundaries
Some traders try to force range trades in markets that don’t have well-defined support and resistance. If you need to squint at the chart or debate where the boundaries are, the range isn’t clear enough to trade.
2. Ignoring Breakout Signals
Ranges don’t last forever. When a market breaks out with strong volume and momentum, continuing to fade the breakout (betting it will fail) is a costly mistake. Respect breakouts and either stay flat or trade in the direction of the break.
3. Overtrading the Range
Just because a range exists doesn’t mean you should take every touch of support or resistance. Wait for high-quality setups with confirmation signals rather than entering on every test of the boundaries.
4. Poor Position Sizing
New range traders often risk too much capital, assuming the range will hold. Remember that all ranges eventually break, and any single trade could be the one where the breakout occurs.
5. Neglecting Transaction Costs
Range trading involves more frequent trades than trend following. Commissions, spreads, and slippage eat into profits quickly. Ensure your expected profit from the range width exceeds your costs by at least 3:1.
Frequently Asked Questions About Range Trading
What is range trading and how does it work?
Range trading is a strategy where traders buy at support levels and sell at resistance levels when prices move sideways within a defined range. The market consolidates between these boundaries, creating predictable buy and sell opportunities. Traders profit from the oscillation between support and resistance rather than from directional trends.
How do I identify a good trading range?
Look for clear horizontal support and resistance levels with at least 2-3 touches on each boundary. The range should show consistent price bounces without breaking through either level. Ensure the range is wide enough to provide profit potential after transaction costs, and verify that volume remains relatively stable within the range.
What is the difference between box range trading and opening range strategy?
Box range trading refers to trading within established support and resistance boundaries over any timeframe, where the boundaries are parallel and well-defined like a rectangle. Opening range strategy specifically trades the high and low established during the first 15-60 minutes of the trading session. Both are range trading methods, but they focus on different time periods and range formations.
When should I avoid range trading?
Avoid range trading during trending markets where prices consistently make higher highs and higher lows (uptrend) or lower highs and lower lows (downtrend). Also stay out during major news events, periods of very low liquidity, when the range is too narrow to cover transaction costs, or when you observe multiple false breakouts suggesting an imminent true breakout.
What risk management rules should I follow for range trading?
Set stop losses just outside the range boundaries to limit losses if the range breaks. Risk no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital per trade. Use proper position sizing based on your stop loss distance. Exit immediately if the range breaks with strong momentum and high volume. Consider taking partial profits at the midpoint of wide ranges to lock in gains.
Start Your Range Trading Journey Today
Range trading offers beginners a structured, methodical approach to profiting from sideways markets. Unlike trend following strategies that require patience and large directional moves, range trading provides frequent opportunities with clearly defined entry and exit points.
The key to success lies in proper range identification, patient execution, strict risk management, and knowing when to step aside. Remember that markets spend the majority of their time in ranges, making this strategy relevant across all timeframes and asset classes.
Start by paper trading your range trading strategy before risking real capital. Observe how ranges form, how boundaries hold or break, and how your timing affects profitability. With practice and discipline, range trading can become a core component of your trading toolkit.
Ready to master range trading? Join our Day Trading Courses for Beginners and learn advanced range trading techniques from professional traders. Get access to live trading examples, detailed chart analysis, and personalized trading mentorship.

Cameron has over 10 years experience in teaching people how to day trade the futures markets. He has feature alongside the CME Group, and NinjaTrader, and has been published in multiple magazines, including leading trading magazine Your Trading Edge magazine.