Derivatives have become one of the most widely traded financial instruments in the world, but many traders find them confusing at first. Whether you’re looking to hedge your portfolio, speculate on price movements, or diversify your trading strategy, understanding derivatives is essential for anyone serious about trading. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about derivative trading, from the basic concepts to practical applications in today’s markets.
Quick Answer: What Are Derivatives?
Derivatives are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, or indices. Rather than buying the asset itself, traders enter into agreements based on the asset’s future price movements.
Common types include futures contracts, options, and swaps, traded either on exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC). Derivatives allow traders to speculate on price changes, hedge existing positions, and leverage their capital without owning the underlying asset.
What Are Derivatives in Trading?
Derivatives are financial contracts between two or more parties where the value depends on the performance of an underlying asset. The derivatives meaning is quite literal—these instruments “derive” their worth from something else, whether it’s a stock index, commodity, currency pair, or interest rate.
Think of derivatives as a promise or agreement about the future. Instead of purchasing gold bars, for example, you could trade gold futures—a derivative that tracks gold’s price. You’re not holding physical gold; you’re holding a contract that moves in value as gold prices change.
The derivatives market has grown exponentially over recent decades, with traders using these instruments for three primary purposes:
- Speculation: Taking positions to profit from anticipated price movements
- Hedging: Protecting existing positions from adverse price changes
- Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences across markets
For traders focused on futures markets, understanding derivatives is particularly crucial since futures contracts are themselves a type of derivative security. The leverage and flexibility these instruments offer make them attractive to day traders seeking to maximize their capital efficiency.
Types of Financial Derivatives
The derivatives market encompasses several distinct instrument types, each with unique characteristics and trading applications. Let’s examine the main categories:
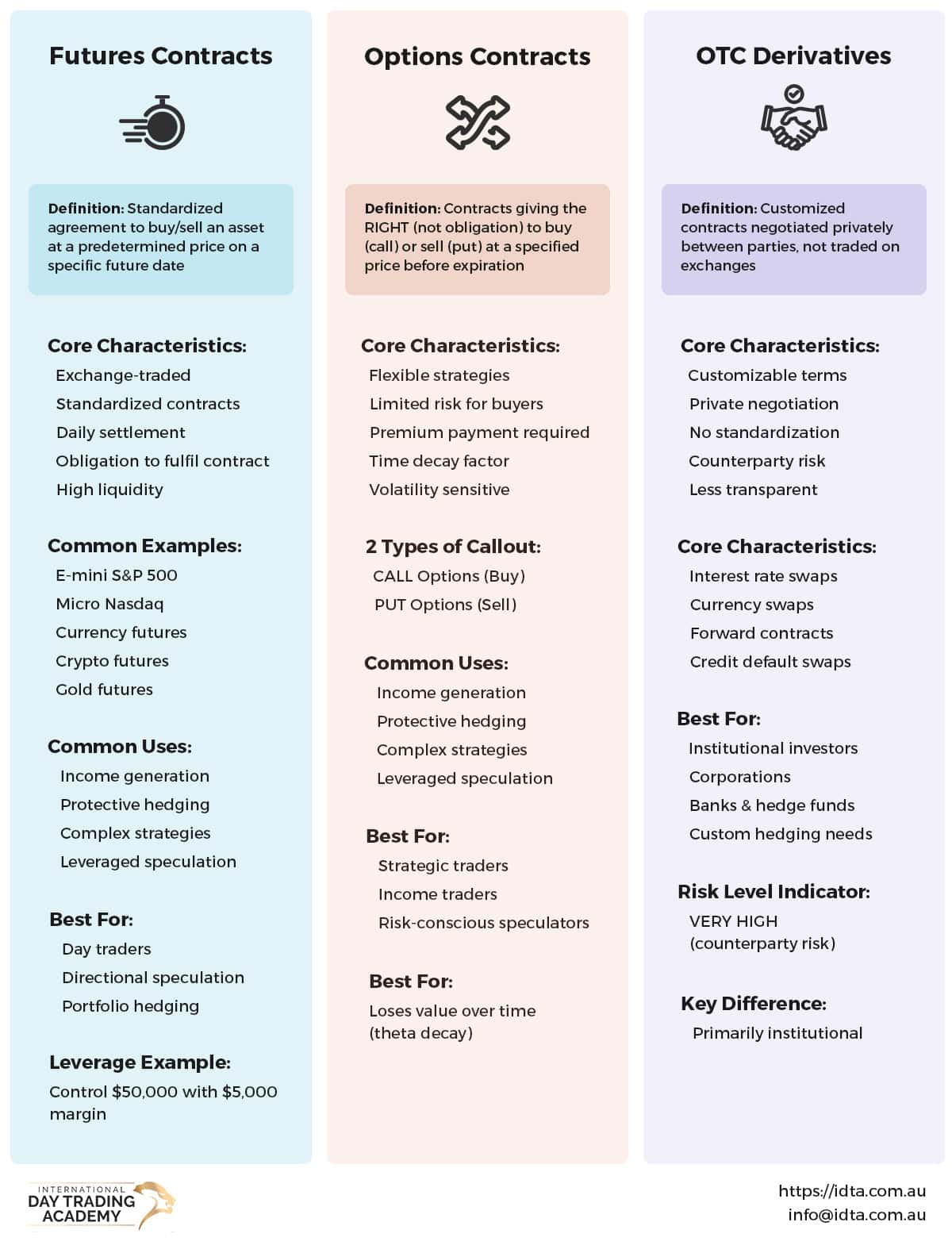
Futures Contracts
Futures are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Unlike informal agreements, futures contracts trade on regulated exchanges with standardized terms, making them transparent and accessible.
Key features include:
- Standardized contract sizes and expiration dates
- Exchange-traded with clearinghouse guarantees
- Daily settlement through mark-to-market procedures
- High liquidity in major markets
Futures are particularly popular among day traders because they offer leverage, extended trading hours, and the ability to profit in both rising and falling markets. Micro futures contracts have made this market accessible even to traders with smaller accounts.
Options Contracts
Options give buyers the right—but not the obligation—to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an asset at a specified price before expiration. The seller of the option has the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises their right.
Options provide several strategic advantages:
- Limited risk for buyers (premium paid)
- Flexibility to profit from various market conditions
- Ability to generate income through option selling
- Complex strategies for sophisticated traders
Swaps and OTC Derivatives
While swaps are more common in institutional trading, understanding OTC derivatives helps traders appreciate the broader market landscape. OTC derivatives are customized contracts traded directly between parties rather than on exchanges. Interest rate swaps and currency swaps are typical examples used primarily by corporations and financial institutions for risk management.
How the Derivatives Market Works
The derivatives market operates through two primary channels: exchange-traded derivatives and over-the-counter (OTC) transactions.
Exchange-Traded Derivatives
Major exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), and Eurex facilitate standardized derivative trading. These exchanges operate under strict regulatory oversight from bodies like the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), ensuring market integrity and trader protection.
These platforms provide:
- Transparent pricing through centralized order books
- Clearinghouse protection against counterparty default
- Regulatory oversight and standardized contracts
- Real-time market data and historical information
For day traders, exchange-traded derivatives offer the advantage of liquidity and price discovery. You can enter and exit positions quickly during market hours, essential for strategies that capitalize on short-term price movements.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Derivatives
The OTC derivatives market involves customized contracts negotiated directly between parties. While institutional traders frequently use OTC markets for tailored solutions, retail traders typically stick with exchange-traded instruments due to their accessibility and lower risk.
Understanding both markets helps traders recognize opportunities and limitations. For instance, while you might trade standard futures contracts for day trading, larger portfolio managers might use OTC derivatives for specific hedging needs that standardized contracts can’t address.
Benefits of Trading Derivatives
Derivative trading offers several compelling advantages that explain their popularity among active traders:
Capital Efficiency Through Leverage
Derivatives allow you to control large positions with relatively small capital outlays. Through margin requirements, you might control $50,000 worth of an index with just $5,000 in your account. This leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses, making risk management crucial.
When trading futures, understanding proper position sizing relative to your account becomes essential. Overleveraging remains one of the primary reasons traders fail, so always respect the power that derivatives give you.
Flexibility to Profit in Any Market Direction
Unlike traditional investing where you typically buy and hope for appreciation, derivatives let you profit whether markets rise or fall. Going short is just as straightforward as going long, providing opportunities regardless of market trends.
This flexibility is particularly valuable for day traders who focus on short-term price movements rather than long-term directional bias. You can adapt to changing market conditions throughout the trading session.
Portfolio Hedging and Risk Management
Derivatives serve as powerful hedging tools. If you hold a stock portfolio and worry about short-term volatility, you could sell index futures as a hedge. If the market falls, gains on your short futures position offset losses in your stock holdings.
Professional traders often use this hedging capability to protect profits or reduce risk during uncertain periods without completely liquidating positions.
Access to Diverse Markets
Through derivatives, traders can access markets that might otherwise be difficult or expensive to trade. Want exposure to crude oil prices? Trade energy futures. Interested in international markets? Currency futures provide straightforward access without complex foreign exchange procedures.
Risks and Considerations in Derivative Trading
While derivatives offer significant advantages, they also carry risks that every trader must understand and manage:
Leverage Risk
The same leverage that amplifies profits equally amplifies losses. A small adverse price movement can wipe out your initial margin and potentially more if you don’t use protective stops. Never trade with capital you can’t afford to lose, and always implement robust risk management strategies.
Market Volatility
Derivatives can experience rapid price swings, especially during news events or economic releases. This volatility creates opportunities but also increases the risk of significant losses if you’re caught on the wrong side of a move.
Successful traders develop the discipline to accept losses quickly and protect their capital. As emphasized in trading education, managing your exits is just as important as identifying entry points.
Complexity and Learning Curve
Understanding contract specifications, expiration mechanics, and pricing dynamics requires education and practice. Many new traders jump into derivative markets without adequate preparation and quickly lose money.
Before trading with real capital, invest time in education and practice with simulators. Understanding how futures contracts work and practicing your strategy in real market conditions without financial risk provides invaluable experience.
Time Decay and Expiration
Options contracts lose value as expiration approaches due to time decay, and futures contracts have fixed expiration dates requiring you to roll positions or close them. Managing these time-sensitive aspects adds complexity to your trading.
Getting Started with Derivatives Trading
If you’re ready to explore derivative trading, follow these steps to build a solid foundation:
1. Build Your Knowledge Base
Start with comprehensive education covering market fundamentals, technical analysis, and trading psychology. Understanding concepts like support and resistance becomes crucial when making trading decisions in fast-moving derivative markets.
Quality education from experienced traders can dramatically shorten your learning curve and help you avoid common mistakes.
2. Choose Your Market Focus
Rather than trying to trade everything, focus on specific markets. Many successful day traders specialize in particular futures contracts like index futures (E-mini S&P 500, Micro Nasdaq) or commodity futures.
Specialization allows you to develop deep understanding of how your chosen market behaves, recognize patterns, and make better-informed trading decisions.
3. Develop a Trading Plan
Your trading plan should specify:
- Which derivative instruments you’ll trade
- Your entry and exit criteria
- Position sizing rules
- Daily loss limits and profit targets
- Trading hours and session focus
A comprehensive trading journal helps you track performance, identify patterns in your decision-making, and continuously improve your approach.
4. Practice Before Going Live
Use simulation accounts to practice your strategy in real market conditions. This practice phase helps you:
- Familiarize yourself with platform functionality
- Test your strategy without financial risk
- Build confidence in your decision-making process
- Identify weaknesses in your approach
5. Start Small and Scale Gradually
When you begin trading with real capital, start with the smallest contract sizes available. Micro futures contracts provide an excellent entry point, allowing you to trade with manageable risk while gaining experience.
As your confidence and consistency grow, you can gradually increase position sizes while maintaining disciplined risk management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between derivatives and stocks?
Derivatives are contracts based on underlying assets, while stocks represent ownership in companies. When you buy stocks, you own a piece of the company; with derivatives, you’re entering a contract based on an asset’s price movements without owning it. Derivatives typically offer higher leverage and can be used to profit from falling prices more easily than traditional stock trading.
Are derivatives suitable for beginner traders?
Derivatives can be suitable for beginners who approach them with proper education and risk management. Start with comprehensive training, practice extensively with simulation accounts, and begin with smaller contract sizes like micro futures. The leverage in derivatives makes education and discipline even more critical than in traditional investing. Many successful traders started with proper education and support through structured programs.
How much capital do I need to start trading derivatives?
Capital requirements vary by derivative type and broker. For futures trading, micro contracts allow you to start with as little as $500-$1,000, though most traders benefit from having $2,000-$5,000 to manage risk properly. Remember that your account size should allow you to trade comfortably within your risk parameters without overleveraging your positions.
Can I lose more than my initial investment trading derivatives?
With futures contracts, losses can theoretically exceed your initial margin if positions move significantly against you before being closed. However, most brokers provide protections like automatic liquidation when account equity falls too low. Using stop-loss orders and maintaining proper position sizing relative to your account helps prevent catastrophic losses. Options buyers have limited risk (premium paid), while options sellers face potentially unlimited risk.
What are the best derivatives for day trading?
Popular derivatives for day trading include index futures (E-mini S&P 500, Nasdaq, Dow), micro futures versions of major indices, currency futures, and energy contracts like crude oil. The “best” derivative depends on your strategy, risk tolerance, and trading capital. Most day traders focus on highly liquid markets with consistent volatility and tight bid-ask spreads.
How do I choose between futures and options for trading?
Futures work well for traders seeking direct exposure to price movements with straightforward profit/loss mechanics. Options offer more complex strategies and limited risk for buyers but require understanding of time decay and volatility. Many day traders prefer futures for their simplicity, liquidity, and leverage. Your choice should align with your trading goals, experience level, and strategy requirements.
Conclusion: Your Path Forward in Derivatives Trading
Derivatives represent powerful tools for traders seeking to profit from market movements, hedge portfolios, or access markets with capital efficiency. While the leverage and flexibility of derivative securities create significant opportunities, they also demand respect, education, and disciplined risk management.
Success in derivative trading doesn’t happen overnight. It requires comprehensive education, extensive practice, and ongoing commitment to improvement. By understanding how derivatives work, managing your risk appropriately, and focusing on developing consistent trading skills, you can harness these instruments to achieve your trading goals.
Whether you’re interested in day trading futures, exploring options strategies, or simply diversifying your trading approach, the key is to start with solid education from experienced professionals. Many traders find that structured learning environments with mentorship and community support accelerate their progress and help them avoid costly mistakes.
Ready to take your trading to the next level? Explore professional trading education designed for traders at all levels, from complete beginners to those looking to refine their derivative trading strategies. Join a free trading class to discover how professional traders approach the derivatives market and build consistent trading skills.

Cameron has over 10 years experience in teaching people how to day trade the futures markets. He has feature alongside the CME Group, and NinjaTrader, and has been published in multiple magazines, including leading trading magazine Your Trading Edge magazine.